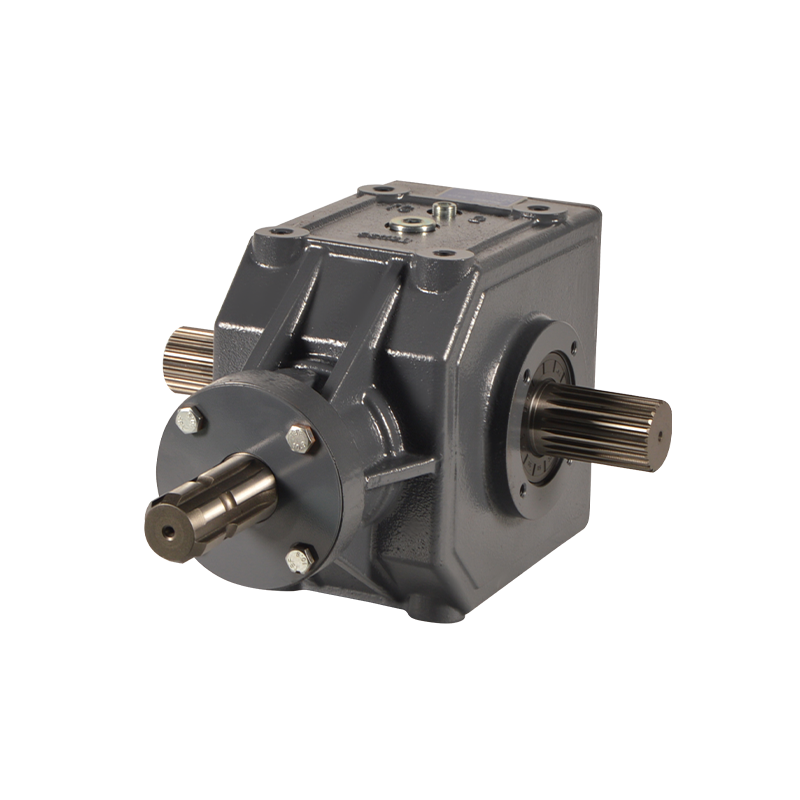
The fertilizer seeder type gearbox is a vital component in modern agricultural machinery, designed to handle the varying power needs of fertilizer spreaders and seeders. These machines are built to distribute seeds and fertilizers evenly across farmland, significantly impacting crop yield and quality. As different crops, soil conditions, and operational requirements demand precise control over seed placement and fertilizer distribution, the gearbox must be versatile enough to adapt to these changing needs. So, how does the gearbox effectively manage the fluctuating power requirements when adjusting the speed and depth of fertilizer spreading or seeding?
At its core, the gearbox operates on an advanced transmission system that uses gears to deliver consistent power across different components. The beauty of this design lies in its ability to modify key parameters like speed, spacing, and depth. This adaptability is crucial for optimizing the application of fertilizers and seeds based on the specific conditions of each field. For example, in looser soils, more power may be needed to achieve deeper seed penetration, while in compacted soils, the system must adjust to distribute fertilizer and seeds at a shallower depth. The gearbox ensures that these adjustments are made seamlessly, without compromising the uniformity or efficiency of the operation.
The gearbox is engineered to withstand the stress of varying loads and external impacts, which are common in agricultural settings. Whether it’s mud, rough terrain, or continuous heavy-duty use, the gearbox is built to endure, ensuring that power is transmitted effectively to different parts of the machine. This resilience is key in handling varying power requirements. When the machinery adjusts its operation, whether for a faster speed or deeper sowing, the gearbox’s robust construction ensures that the power is smoothly transferred, reducing energy loss and preventing mechanical failure. It optimizes power transmission, which not only ensures the longevity of the machinery but also boosts overall operational efficiency. The gearbox can accommodate power changes without experiencing strain, thus avoiding sudden performance dips or failures.

Moreover, the gearbox’s ability to adjust power for different spreading and sowing depths contributes to the customization of agricultural operations. Operators can tailor their machinery to specific crops or soil conditions, ensuring that the spread rate and depth align with the needs of the plants and the soil structure. This customization is achieved through a combination of gear ratios and settings that adjust according to the farmer’s input. The gearbox thus plays a pivotal role in enabling precision agriculture, where every aspect of the farming process, from fertilizer application to seeding depth, can be fine-tuned for maximum crop production.
In addition to its adaptability, the gearbox ensures smooth operation even under harsh conditions. Agricultural operations often require machinery to run in challenging environments, with mud, uneven terrain, and constant load variations. A well-designed gearbox incorporates high-quality materials and a sturdy structure, which ensures that it can endure these rough conditions while maintaining efficient performance. The gearbox also enhances fuel efficiency and minimizes power loss, allowing operators to get more out of each operation while maintaining energy efficiency. The key to its reliability lies in its ability to balance the power demands of the system, adjusting dynamically to different tasks without overwhelming the machine’s components.
The fertilizer seeder type gearbox is much more than just a power transmission system; it is the backbone of precision seeding and fertilizer spreading. By adjusting to the varying power demands of different field conditions, crop types, and operational settings, it plays a crucial role in ensuring that agricultural machinery works efficiently, effectively, and consistently. The gearbox’s ability to smoothly handle changes in speed, spacing, and depth of application ensures that every job is done with precision, reducing waste, increasing crop yields, and ultimately enhancing the profitability of agricultural operations.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى русский
русский Español
Español